Language Support in the Editor
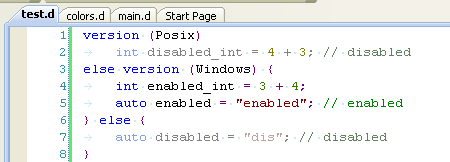
Syntax Highlighting
- semantic syntax highlighting supports all kinds of types and variables.
The colors are configured in the standard Visual Studio dialog Tools->Options->Environment->Fonts and Colors. This code snippet shows how the color names match the respective code.
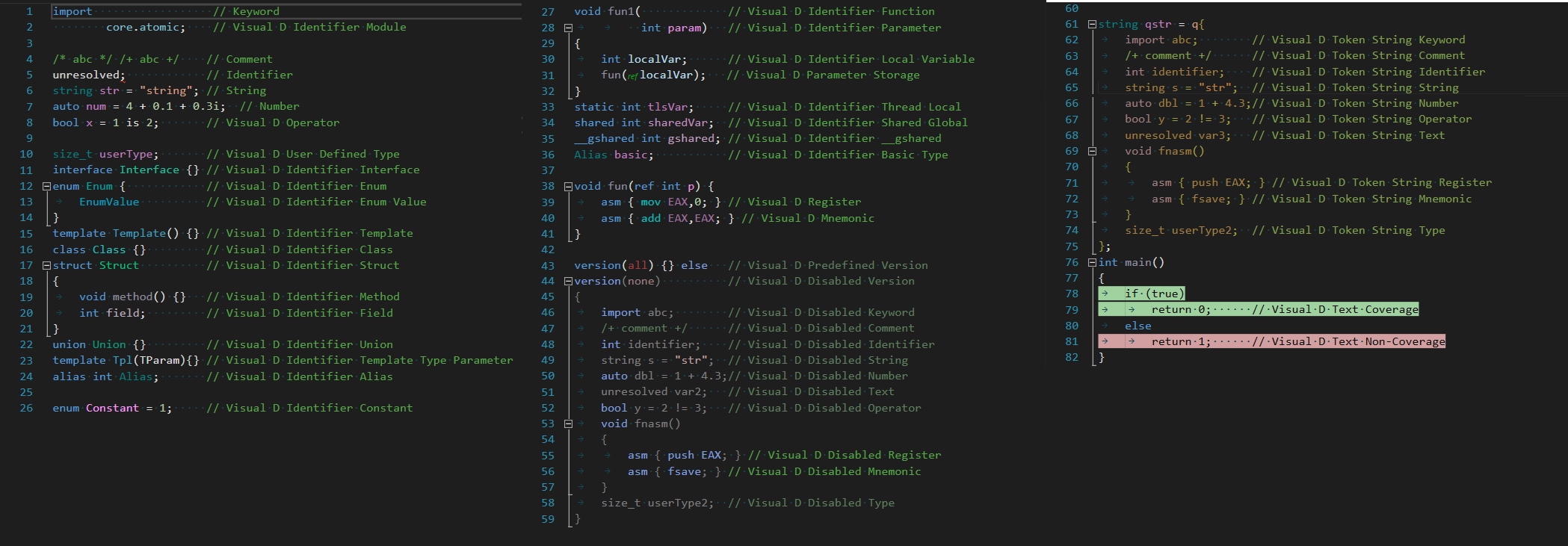
- all sorts of D2 style strings are supported.
- statements disabled by version or debug conditionals are displayed in a slightly different color. Debug and version identifiers and levels can be defined in the same source file or in the current project configuration. The compiler predefined version identifiers are also recognized.
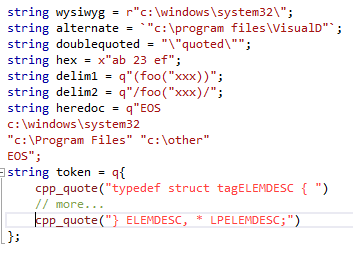
- code in token string literals are highlighted in another slightly different color than regular code.
- highlighting colors can be setup in the "Fonts and Colors" page found in the Tools->Options Dialog. In addition to the regular colors, you'll find "Visual D Disabled ..." colors for the code disabled through version statements and "Visual D Token String ..." colors for the code in token strings.
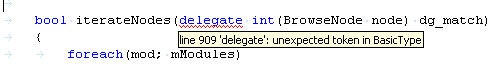
- underlining of syntax and semantic errors (semantic analysis done when using the dmd based engine)
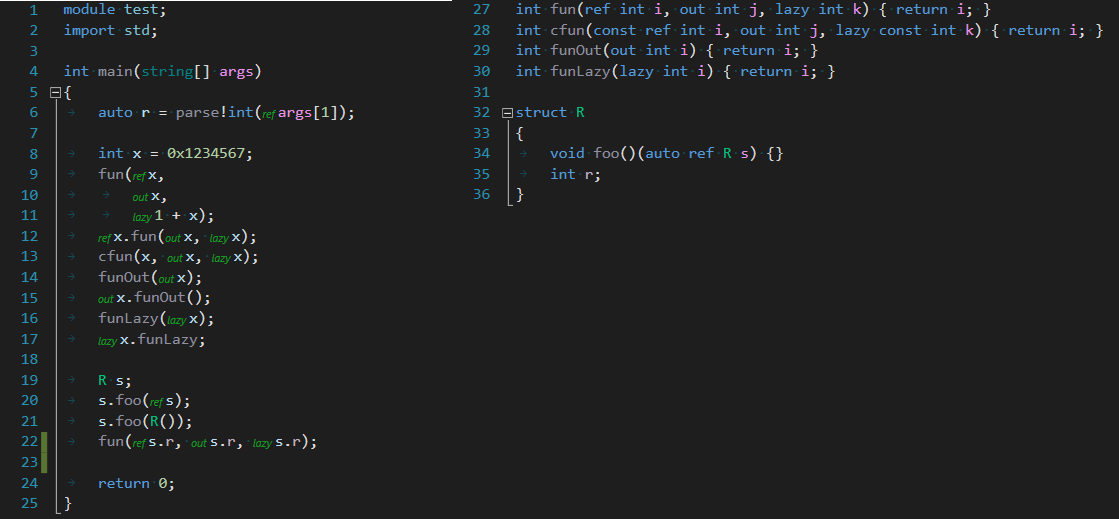
new in Visual D 1.1: parameter storage mutable ref/out/lazy can be shown at the call site.
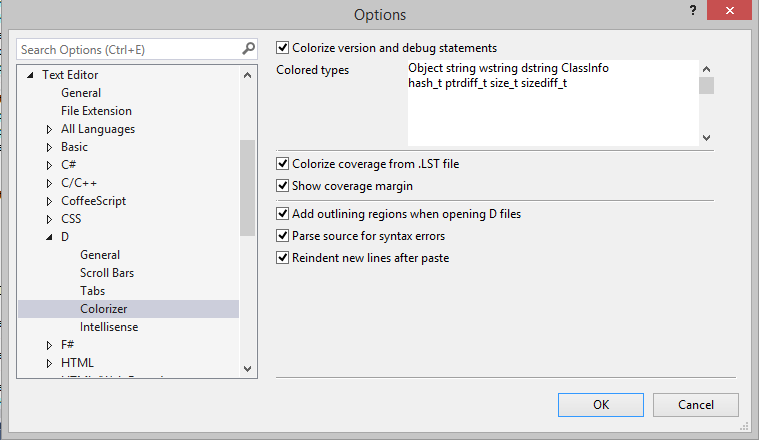
The colorizer can be configured in the "Editor" setup page of the language settings in Tools->Options->Text Editor->D->Editor:
You can manipulate coloring of identifiers by assigning them to a different color category: if prefixed with one of the section names, they will be highlighted accordingly. The available color categories are:
- [Keyword] color used by all languages
- [Comment] color used by all languages
- [Identifier] color used by all languages
- [String] color used by all languages
- [Number] color used by all languages
- [Text] any other text not falling into the other categories (color used by all languages)
- [Operator] Visual D specific operators
- [Register] Visual D specific registers in inline assembler
- [Mnemonic] Visual D specific mnemonics in inline assembler
- [Type] Visual D specific user specified identifiers
- [Version] predefined version identifiers
Without any section given, [Type] is assumed. Here's an example how to map "string" to keyword coloring:
[Keyword] string
Code Completion and Navigation
Selecting "Open Language options" from the Visual D Menu will take you directly to the global options page for code completion.
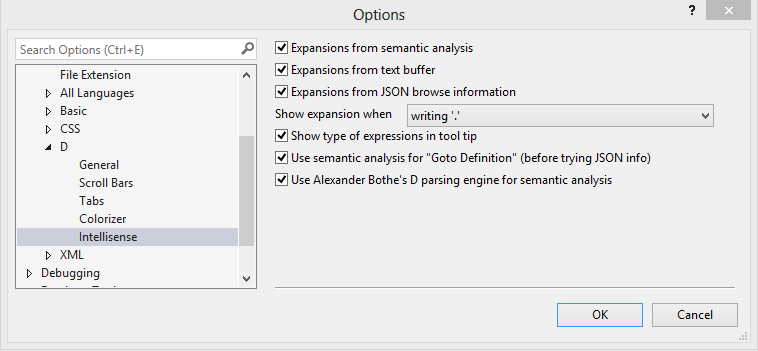
- Expansions from semantic analysis: the semantic engine will try its best to figure out the current scope of the edited text and find valid identifiers. If no matching identifier is found or if you trigger expansion again, expansions from the text buffer or JSON browse information will be added.
- Expansions from text buffer: completion will show identifiers in the vicinity of the caret from the same buffer (default short-cut Ctrl-Space). If no matching identifier is found or if you press the short-cut again, identifiers from JSON files are also displayed.
- Expansions from JSON browse information: completion will show matching identifiers from the compiler generated JSON files. No information about the current edit scope will be used.
- Show expansion when: sets the trigger for showing the code completion popup. Using a mode that displays completion more often also includes the other triggers, i.e. hitting Ctrl+Space is always possible to display completions.
- Show type of expressions in tool tip: Display information about the hovered identifier in a tool tip.
- Use semantic analysis for "Goto Definition": goto definition (default short-cut F12) can either request the location of the definition of a symbol from the semantic engine or takes information from compiler generated JSON files. A successful build with JSON output enabled is necessary for the latter. JSON files can also be precompiled and placed into the directories given in the global options. If there are multiple definitions for the identifier at the caret position, the Search Window will show up.
- Use Alexander Bothe's D parsing engine: Use the semantic engine that also powers Mono-D and D-IDE. It is a bit outdated, but runs on a 32-bit machine. You must have installed it from within the Visual D installer.
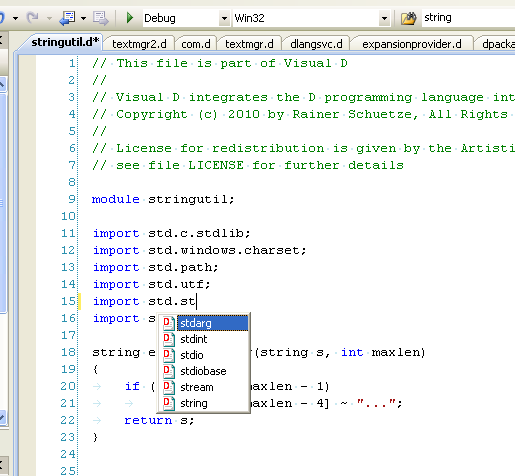
Triggering completion an import statement will always complete the token from the files and folders available in the import directories.
More features
You might want to check the following features:- smart indentation will indent nicely after pressing Return.
- comment/uncomment a selection of lines
- highlight/jump-to matching braces (default shortcut Ctrl-´)
- code snippets: let's you select from a list of snippets, some of them allowing token
replacements (default shortcut Ctrl-K Ctrl-X). You can also insert code-snippets by writing its
shortcut, then pressing the key for command "Edit.!InvokeSnippetFromShortcut". For example,
shortcut "for" yields

- parameter info tooltips (default short-cut Ctrl-Shift-Space) showing function prototype and
highlighting current position in argument list. As with "goto definition" this feature relies
on JSON files being generated.
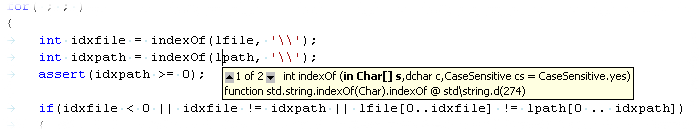
- show scope in status line: to avoid navigating through a larger file to figure out what
class the current function belongs to, command "VisualD.ShowScope" displays the class, function,
etc. at the caret position:
This command is also accessible from the Visual D menu, but it is best to assign it to some keyboard shortcut.
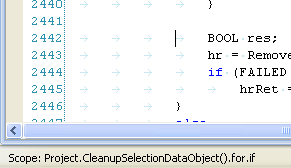
- Outlining of curly braced declarations and statements and multi-line comments
Automatic outlining can be disabled on the global configuration page "Tools->Options->Text Editor->D->Colorizer". Using command "Outlining->Collapse to Definitions" will enable it for the current text buffer.

- Two commands are added to the "Edit->Outlining" menu: "Collapse unittests" will fold away unittest blocks that might obfuscate the actual code if they become excessive. "Collapse disabled code" will hide code blocks actually not compiled due to version or debug conditions helping you concentrate on the active code.
- show the clipboard ring in a context menu to paste from. This operation is invoked by
the "Edit->Cycle Clipboard Ring" command.